What is Bursitis and How Can You Prevent It?
Have you ever gotten pain in your joints and even swelling? It might be bursitis.
Bursitis is the inflammation of a bursa, a small fluid-filled sac that cushions and lubricates the areas between tendons, muscles, and bones. It commonly affects the joints, causing pain, swelling, and limited mobility.
Bursitis Causes
Bursitis is typically caused by repetitive movements or positions that put excessive pressure or friction on the bursa, leading to irritation and inflammation. Some common causes of bursitis include:
Repetitive motions: Activities that involve repetitive motions or positions can contribute to bursitis. Examples include throwing a baseball, gardening, painting, or kneeling for extended periods.
Joint overuse: Overusing a joint or placing excessive stress on it can lead to bursitis. This can occur from activities such as running, jumping, or participating in high-impact sports.
Injury or trauma: Direct injury or trauma to a joint can cause bursitis. This can happen due to a fall, impact, or prolonged pressure on the affected area.
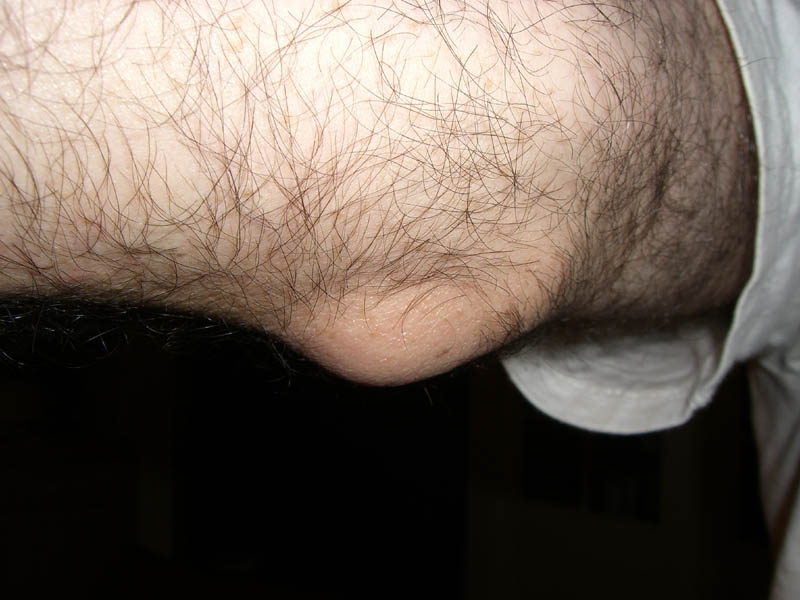
Treating Bursitis
The treatment of bursitis typically involves a combination of self-care measures and medical interventions. Here are some common approaches to treating bursitis:
Rest and immobilization: Resting the affected joint and avoiding activities that exacerbate symptoms can help relieve pain and reduce inflammation. Immobilization may involve the use of slings, braces, or splints.
Ice and heat therapy: Applying cold compresses to the affected area can help reduce swelling and pain. Heat therapy, such as warm compresses, can also provide relief and promote blood flow to the area.
Pain management: Over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help reduce pain and inflammation. In some cases, a healthcare professional may prescribe stronger pain medications.
Physical therapy: Physical therapy may be recommended to strengthen the muscles around the affected joint, improve range of motion, and promote healing. Therapeutic exercises and techniques can help reduce symptoms and prevent recurrence. Those in the Seattle area or in Snohomish County can come to Everett Spine & Rehab for physical therapy as well as chiropractic care.
Injections: In severe cases of bursitis, a healthcare professional may recommend corticosteroid injections to reduce inflammation and provide pain relief. These injections are administered directly into the bursa.
Aspiration: In certain situations, excess fluid may be removed from the bursa through a procedure called aspiration. This can help alleviate pain and reduce swelling.
Preventing Bursitis
Preventing bursitis involves taking certain precautions and adopting healthy habits to reduce the risk of developing the condition. Here are some strategies that can help prevent bursitis:
Avoid repetitive motions: Minimize repetitive movements or positions that put excessive stress on the joints. If your work or activities involve repetitive actions, try to take regular breaks or modify your technique to reduce the strain on the affected areas.
Use proper body mechanics: Practice good posture and body mechanics during activities, whether it’s at work, exercise, or daily tasks. Maintain proper alignment, use ergonomic equipment, and avoid overloading your joints.
Warm up and stretch: Before engaging in physical activities or exercises, warm up your muscles with light aerobic activities and perform dynamic stretching. This helps prepare your body for the demands of the activity and reduces the risk of injury.
Gradual progression: When starting a new exercise program or increasing the intensity or duration of your workouts, do so gradually. This allows your body to adapt and prevents overuse injuries, including bursitis.
Use protective equipment: If you participate in sports or activities that carry a risk of joint injury, use appropriate protective equipment, such as knee pads, elbow guards, or wrist braces. This can help cushion and support the joints, reducing the risk of bursitis.
Maintain a healthy weight: Excess weight places additional stress on the joints, increasing the risk of bursitis. Maintain a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise to reduce the strain on your joints.

Cross-train and vary activities: Engaging in a variety of activities and cross-training can help distribute the workload among different muscle groups and joints. This reduces the repetitive stress on specific areas and decreases the likelihood of developing bursitis.
Listen to your body: Pay attention to any discomfort or pain in your joints. If you experience persistent or worsening symptoms, take a break from the activity and consult with a healthcare professional. Ignoring warning signs can lead to further injury and the development of bursitis.
By incorporating these preventive measures into your daily routine, you can reduce the risk of bursitis and maintain the health and function of your joints. If you have specific concerns or a history of bursitis, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare professional or physical therapist for personalized advice.
Sources